Blockchain Technology: one of the most important tech stories of the past ten years. Everyone is talking about it, but sometimes, its real meaning and how it works need to be explained. Blockchain is known for being impossible to hack, but its basic idea is pretty easy to understand. In addition, it has the power to change whole areas completely.
What is Blockchain?
Blockchain, also called distributed ledger technology (DLT), uses a decentralized network and cryptographic hashing to make the past of any digital asset clear and impossible to change. Comparing it to Google Docs, it’s easy to understand how blockchain works. When shared with a group of people, a Google Doc can’t be copied or moved; instead, it is sent to different people.
This sets up a decentralized distribution network so that everyone can view the main document at the same time. All changes to the document are also recorded instantly so that everyone can see the updates, and no one is locked out while they wait for another party to make changes.
Blockchain Features:
- A blockchain is a database or ledger in which encrypted blocks of data regarding digital assets are kept chained together to create a real-time, single source of truth.
- Instead of being copied and transferred, digital assets are distributed in the form of a ledger.
- Because digital assets are decentralized, several parties on the chain can govern them on a real-time basis.
- Blockchain ledgers are transparent; all changes are recorded by upholding credibility.
- Blockchain technology is a top-notch choice for practically every industry since its ledgers are open to the public and built with built-in security features.
Why does it matter so much?
Decentralized blockchain databases simplify digital asset tracking and corporate network transactions. Physical assets include homes, cars, money, and land, while intangible assets include intellectual property, patents, copyrights, and branding. Blockchain networks can record and trade almost any value, reducing risk and improving efficiency.
Every organization needs data. Fast, accurate delivery is great. Blockchain’s immutable record for permissioned network participants is suited for real-time, transparent data exchange: blockchains record orders, payments, accounts, and production. You can view the entire transaction, boosting your confidence and opening new doors because everyone knows the truth. Walmart, Pfizer, AIG, Siemens, Unilever, and others use blockchain. IBM created the Food Trust blockchain to track food shipments.
Do this. Why? Food companies are plagued by infections from E. coli, salmonella, and listeria. Outbreaks of foodborne illness take weeks to diagnose. Blockchain lets brands track food from origin to delivery and identify all food contaminants. By monitoring everything they touch, these companies can detect issues early and save lives. These are Blockchain implementations.
How does Blockchain work?
A decentralized, safe digital ledger keeps track of all activities on the blockchain. Each transaction is put together in a block, which is tied to the block before it, making a chain. Miners, people who are part of the network, check these blocks by solving cryptographic problems. Once the transaction is confirmed, it is put on the blockchain. This ensures that everything is clear, can’t be changed, and can’t be hacked.
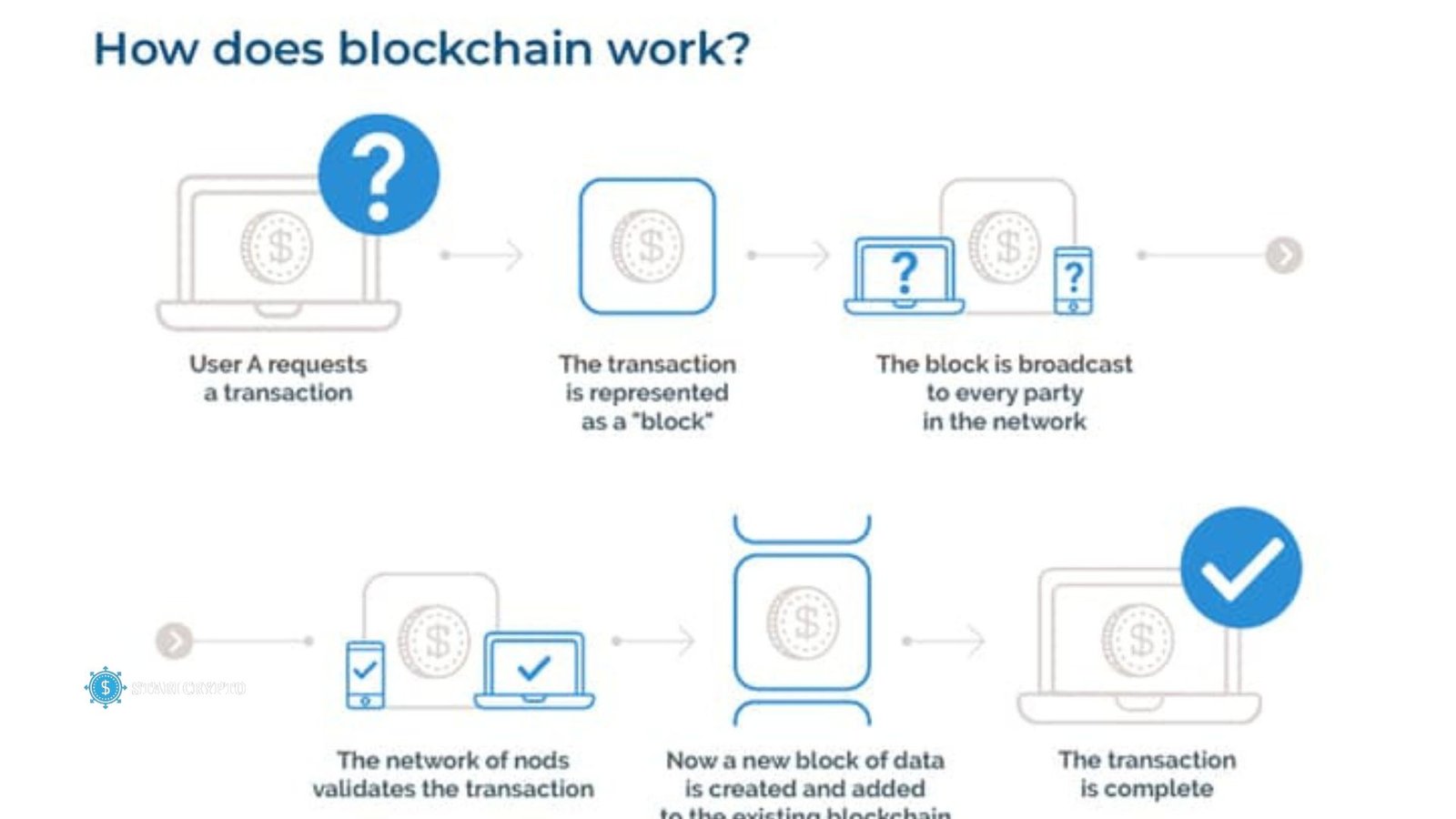
The main ideas behind a blockchain
The word “blockchain” comes from saving information about transactions in blocks that are linked together in a chain. As more activities are added to the Blockchain, it becomes bigger. Blocks are added to the chain and follow the rules set by the network’s users. They copy and confirm the times and orders of transactions.
Each block has a hash, which is a digital record or a unique identification, as well as the hash of the block before it. Since each block is linked to the block before it by its number, it can’t be changed or moved between blocks.
- A ledger. A shared ledger is an “append-only” distributed system of records shared across a business network. By recording transactions once, a shared ledger eliminates the duplication of effort typical of conventional corporate networks.
- Permissions. Transactions are secure, authenticated, and verifiable, thanks to permissions. Organizations can more easily adhere to data protection laws outlined in the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act or HIPAA and the EU General Data Protection Regulation with the option to restrict network participation (GDPR).
- Smart contracts. “An agreement or rules that govern a business transaction; it is kept on the blockchain and is performed automatically as part of a transaction,” according to the definition of a smart contract.
Is Blockchain safe and secure?
Because it is decentralized and uses cryptography, blockchain is thought to be very safe and private. A blockchain has many nodes, or computers, that check transactions. This makes sure that no one person or group owns the data, which makes it hard to change or hack. Each transaction is encrypted and put together into a block. Blocks are tied to blocks that came before them, creating a chain that can’t be changed easily. If you add a transaction to the blockchain, it’s hard to change it without changing all the blocks that come after it, which would take a lot of computing power.

Also, because blockchain is transparent, everyone on the network can see the same information, building trust and responsibility. Even though the technology is safe, it can still be broken by outside causes, like apps that aren’t working right, mistakes made by people, or attacks on exchanges or wallets. As blockchain technology develops, security steps get stronger, making the system even safer.
Also Read: Blockchain Technology in Gaming And New Frontier
Conclusion
Blockchain technology has grown so quickly that it has led to new ideas for social networks and shared storage, among other things. When it comes to security, we are the first. As they make blockchain apps, developers should make security a top priority for their blockchain services and apps.
A blockchain application creator’s to-do list should include risk assessments, threat models, and code analysis, which can include both static code analysis and software composition analysis. A good and safe blockchain app needs to have security built in from the start.
















